Moving an ActiveDirectory Domain Controller to a New Server
In this article, I want to describe the process of migrating an ActiveDirectory domain controller from Windows 2003 to Windows Server 2008.
Before you start, it is recommended that you add the new server to the domain. In general this is not essential but it will be much more convenient.
Source server
Next, you need to make sure that the user, that we’ll use for migration, is in the following groups:
- Enterprise admins
- Schema Admins
- Domain Admins
Next, we take the support folder from the Windows 2008 installation disk, find the adprep folder in it and go to it on the source server. When migrating from 2003 to 2008, you need to take adprep from the 2008th Windows.
Preparing everything for migration:
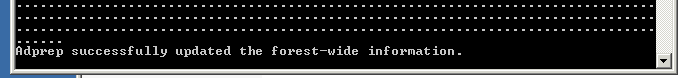
adprep32.exe /forestprep
adprep32.exe /domainprep /gpprep
If the source server has an x64 operating system, then we use the following commands. The first one can take quite a long time:
adprep.exe /forestprep
adprep.exe /domainprep /gpprep
It is also recommended to run the following command. Even if you don’t intend to use Read Only Domain Controllers (RODCs) on your network it will remove unnecessary error messages from the event log.
adprep /rodcprep
Target server
Run in the console
dcpromo
This opens the AD installation window. Click Next.
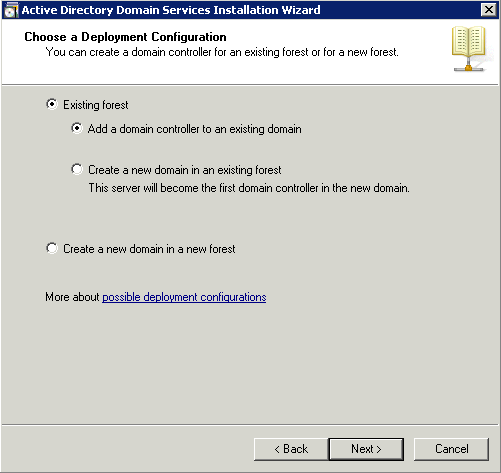
I was adding a controller to an already existing forest so I chose the appropriate item.
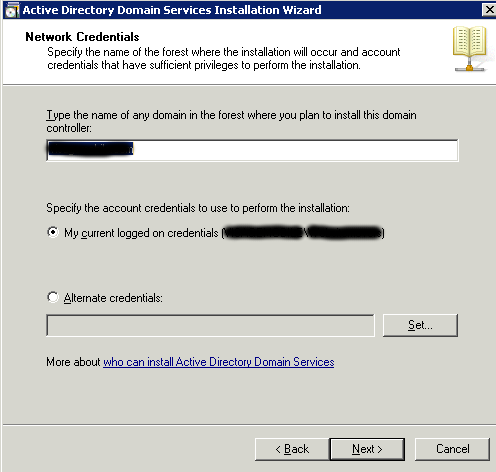
Next the installer will offer the domain name and username from which the service is installed.
Next you will be able to select the site to which the controller should be added. The installation manager itself will suggest this based on the ip address depending on which site the subnet belongs to.
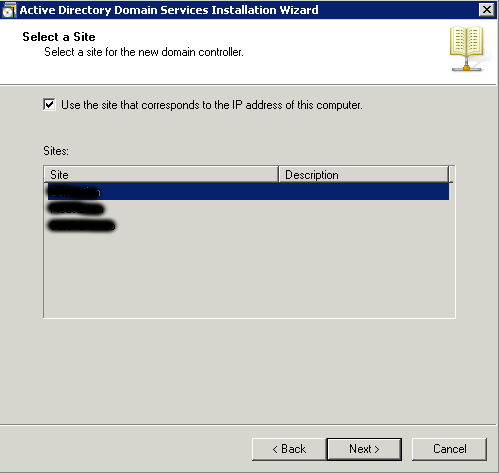
Next-Next-Next
We wait for the wizard to finish and restart the new domain controller.
It is left to transfer the FSMO roles to the new server. To do this, launch a console called Active Directory Schema. To do this, go to the Start menu -> Run. In the window that appears, enter mmc.exe and click OK.
In the window that appears, from the File menu, select the Add/Remove Snap-In item:
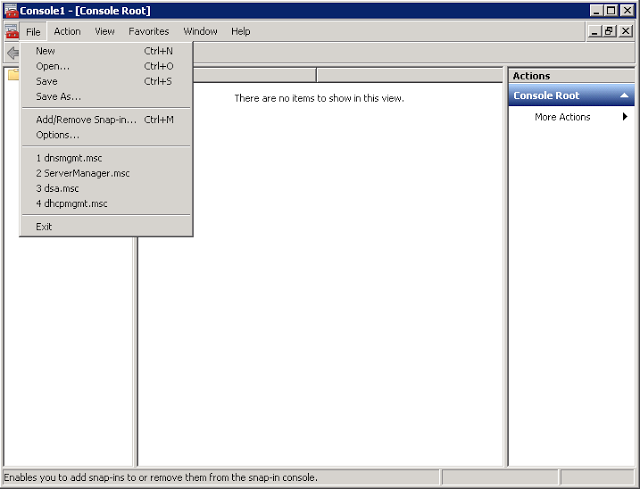
From the list in the left column, select Active Directory Schema, press the Add-> button, then OK.
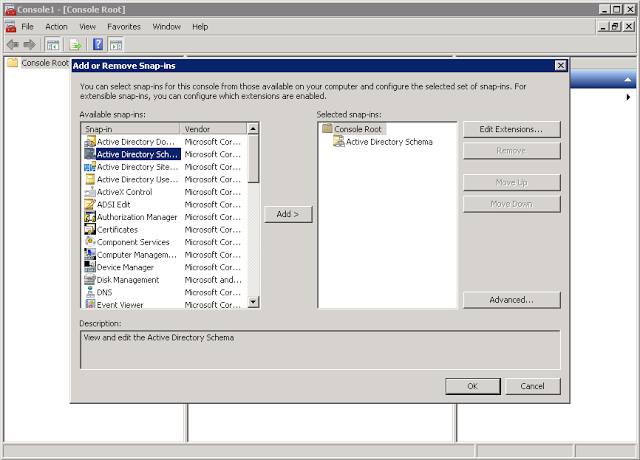
As a result of such gestures the Active Directory Schema element will appear in the left column of the console. Right click and select Change Active Directory Domain Controller.
In the window that appears select the domain controller on which the FSMO roles are spinning:
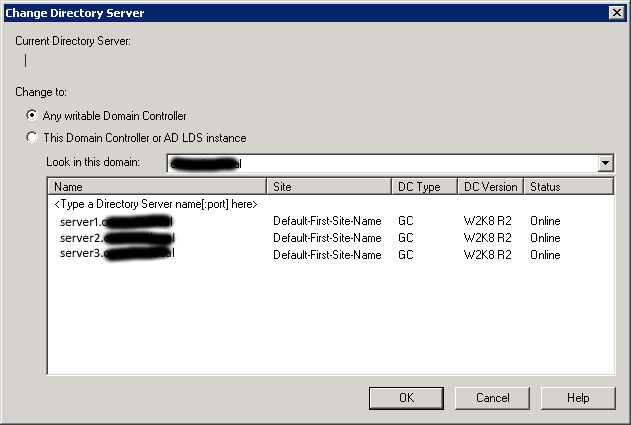
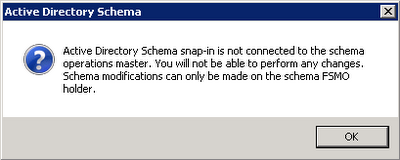
It’s hard to go wrong with the choice. If you select a Domain Controller that does not manage FSMO, you will get this error:
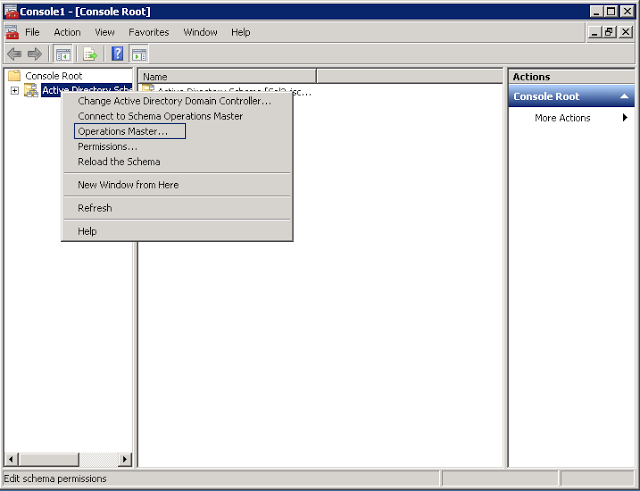
We are now connected to the owner of the master role. Right click on Active Directory Schema and select Operations Master:
In the window, select where to transfer FSMO and click OK.
To transfer the RID, PDC and Infrastructure Master roles, run Active Directory Users and Computers (Start -> Control Panel -> Administrative Tools -> Admin tools). Further, by analogy with the previous step, we connect to the source server. Right-click on Active Directory Users and Computers and select Operations Master. In the window that appears, go to the desired RID, PDC or Infrastructure tab and select a new server for the role.
In order to transfer the DNS role, you need to run the Active Directory Domains and Trusts console. Further, by analogy with the previous step, we connect to the source server. Right-click on Active Directory Domains and Trusts and select Operations Master. In the window that appears, select a new server for the role.
External links: